Contributions to Simulation of Cybersecurity
Lead Investigator
- Jose Padilla (Advisor)
Project Members
- Hamdi Kavak (Collaborator student 2015-2018)
- Daniele Vernon-Bido (Collaborator student 2015-2018)
- Gayane Grigoryan (Collaborator student 2017-2018)
- Saikou Diallo (Collaborator faculty)
- Ross Gore (Collaborator faculty)
Project Dates
2015-2020
Summary
Several studies were conducted as part of this project funded by The Office of the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering. These studies investigated the use of modeling and simulation in cybersecurity. Three notable contributions are as follows:
Simulation for Cybersecurity
Two papers (Kavak et al. 2016 & Kavak et al. 2021) referenced below reviewed the literature to illustrate what modeling and simulation contributions have been made in the cybersecurity domain and what future directions look viable. The current role that simulation plays in cybersecurity: (1) representative environment building, (2) testing, evaluating, and exploring, (3) training and exercises, (4) risk analysis and assessment, and (5) humans in cybersecurity research. For the future, the advancement of collecting and accessing socio-technological data to inform models, the creation of new theoretical constructs, and the integration and improvement of behavioral models are needed to advance cybersecurity efforts.
Wi-Fi Malware Spread
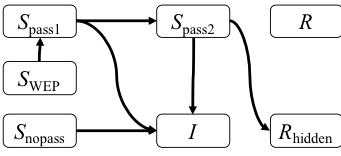
This study (Kavak et al. 2016) revisited an existing Wi-Fi malware spread model with current Wi-Fi router data from WiGLE.net with a refined data selection method. Despite ≈88% WPA adoption rate, we found a rapid malware spread occurring in a week and infecting ≈34% of all insecure routers (≈5.4% of all) after two weeks. This result is significantly higher than the original study projection. It occurs due to the increased use of Wi-Fi routers, causing a more tightly connected graph. We argue that this projected risk can increase, especially when zero-day vulnerabilities are found. Ultimately, thorough consideration is needed to assess cybersecurity risks in the Wi-Fi ecosystem and evaluate interventions to stop digital epidemics.
Modeling Cyber Attackers
This study (Vernon-Bido et al. 2016) explores the impact of attack success rate and social learning on becoming a cyber attacker. An agent-based model is used to depict the effect of interactions of users and attacks of all users, successful and unsuccessful, have on an individual’s decision to become an attacker. The model utilizes rational choice theory, routine activity theory, social learning theory, and perceived behavioral control from the theory of planned behavior to examine factors that move an individual from user to attacker. The model suggests that opportunity has a stronger influence than the rate of successful attacks or the size of the associated group.
Publications & Presentations
- Simulation for Cybersecurity: State of the Art and Future Directions
H. Kavak, J.J. Padilla, D. Vernon-Bido, S.Y. Diallo, R.J. Gore, S. Shetty
Journal of Cybersecurity, 2021, doi:10.1093/cybsec/tyab005
[Paper] [BibTeX] - Assessing the Impact of Cyberloafing on Cyber Risk
D. Vernon-Bido, G. Grigoryan, H. Kavak, and J.J. Padilla
51st Annual Simulation Symposium, Baltimore, MD, April 15-18, 2018, doi: 10.22360/SpringSim.2018.ANSS.020
[Paper] [BibTex] - The Spread of Wi-Fi Router Malware Revisited
H. Kavak, J.J. Padilla, D. Vernon-Bido, R.J. Gore, and S.Y. Diallo
20th Communications and Networking Simulation Symposium, Virginia Beach, VA, April 23-26, 2017
[Paper] [BibTex] - Towards Modeling Factors that Enable an Attacker
D. Vernon-Bido, J.J. Padilla, S.Y. Diallo, H. Kavak, and R.J. Gore
Summer Simulation Conference Montreal, Quebec, Canada, July 24-27, 2016
[Paper] [BibTex] - A characterization of cybersecurity simulation scenarios
H. Kavak, J.J. Padilla, D. Vernon-Bido, S.Y. Diallo, and R.J. Gore
19th Communications and Networking Simulation Symposium, Pasadena, CA, April 3-6, 2016
[Paper] [BibTex]
Funding
- The Office of the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering (OASD(R&E)) under agreement number FAB750-15-2-0120.
Last updated on Jan 29, 2022.