Verification and Validation Methodological Contributions (Pre 2021)
Contributors
- Hamdi Kavak
- Christopher Lynch
- Ross Gore
- Daniele Vernon-Bido
- Saikou Diallo
- Jose Padilla
Dates
2016-2020
Summary
This page summarizes some contributions to the verification and validation of simulation models from my collaborations prior to 2021.
Identifying Unexpected Behaviors of Agent-based Models
Verification and validation (V&V) techniques commonly require modelers to collect and statistically analyze large amounts of data which require specific methods for ordering, filtering, or converting data points. Modelers need simple, intuitive, and efficient techniques for gaining insight into unexpected behaviors to help in determining if these behaviors are errors or if they are artifacts resulting from the model’s specifications. We present an approach to begin addressing this need by applying heat maps and spatial plots to visually observe unexpected behaviors within agent-based models. Our approach requires the modeler to specify hypotheses about expected model behavior. Agent level outputs of interest are then used to create graphical displays to visually test the hypotheses. Visual identification of unexpected behaviors can direct focus for additional V&V efforts and inform the selection process of follow-on V&V techniques. We apply our approach to a model of obesity.
Challenges in Simulation Verification
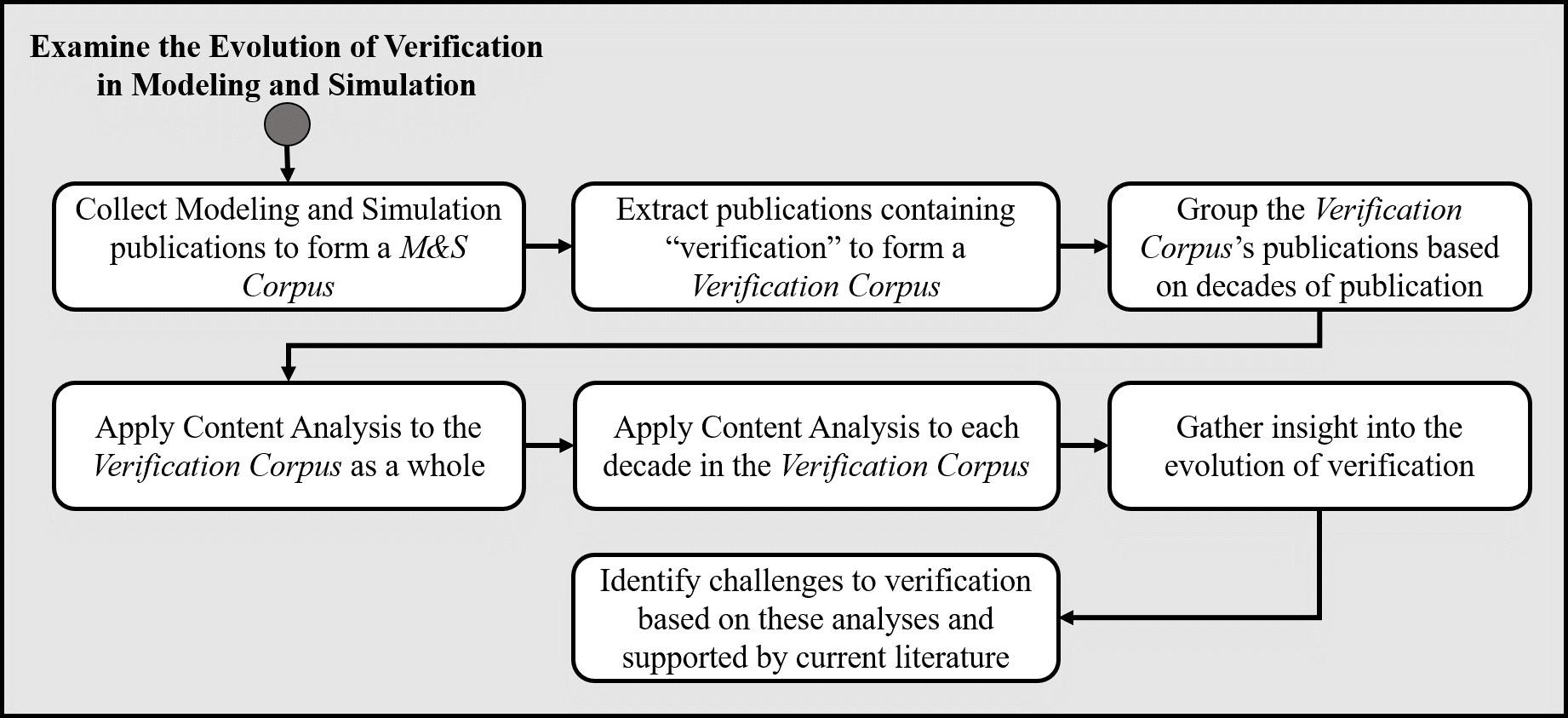
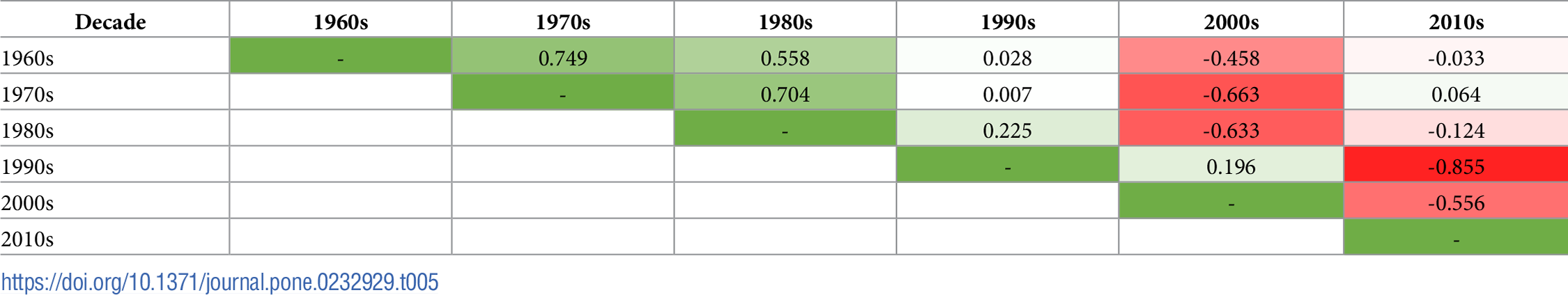
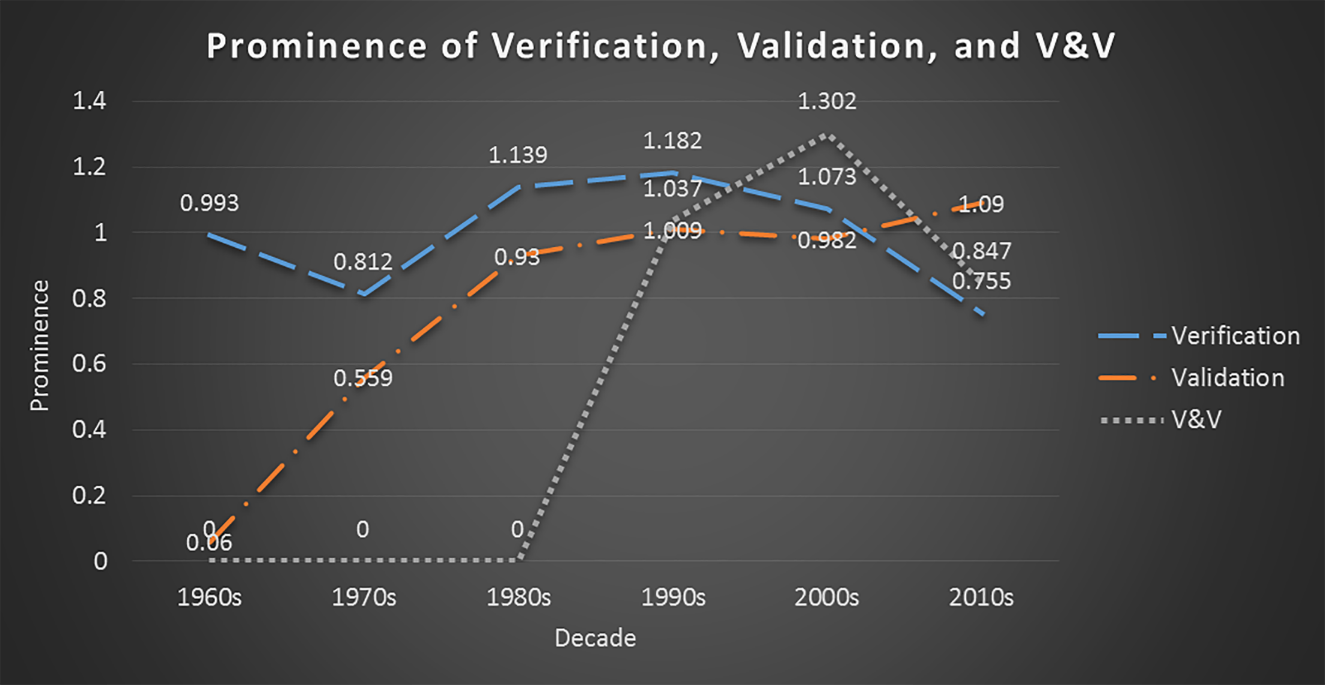
This study explores semantic changes to the concept of simulation verification over the past six decades using a data-supported, automated content analysis approach. We collect and utilize a corpus of 4,047 peer-reviewed Modeling and Simulation (M&S) publications dealing with a wide range of studies of simulation verification from 1963 to 2015. We group the selected papers by the decade of publication to provide insights and explore the corpus from four perspectives: (i) the positioning of prominent concepts across the corpus as a whole; (ii) a comparison of the prominence of verification, validation, and Verification and Validation (V&V) as separate concepts; (iii) the positioning of the concepts associated explicitly with verification; and (iv) an evaluation of verification’s defining characteristics within each decade. Our analysis reveals unique characterizations of verification in each decade. The insights gathered helped identify and discuss three categories of verification challenges as avenues of future research, awareness, and understanding for researchers, students, and practitioners. These categories include conveying confidence and maintaining ease of use; techniques’ coverage abilities for handling increasing simulation complexities; and new ways to provide error feedback to model users.
V&V Calculator
The verification and validation of Agent-based Models (ABMs) is challenging. The underlying structure of the model and the agents can change over time. Furthermore, the theoretical context of the model is often very different from established models of the same phenomenon. In an effort to overcome these issues, Trace Validation is becoming a common V&V mechanism within the Agent-based Modeling community. In Trace Validation, the characteristics of agents and the model are tracked over time and then analyzed by subject matter experts (SMEs) to gain insight into unexpected and potentially invalid output. In a study published by Gore, Lynch, Kavak (2016), we present our tool, the V&V Calculator, which applies predicates employed in the field of software engineering. The result is a structured trace validation approach with quantifiable measures that facilitates SME exploration and insight into the causes of unexpected output within ABMs.
Publications & Presentations
- A content analysis-based approach to explore simulation verification and identify its current challenges
C.J. Lynch, S.Y. Diallo, H. Kavak, J.J. Padilla
PLOS One, 2020, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0232929
[Paper] [BibTeX] - Applying Statistical Debugging for Trace Validation of Agent-Based Models
R.J. Gore, C.J. Lynch, H. Kavak
SIMULATION: Transactions of The Society for Modeling and Simulation International, 2016, doi:10.1177/0037549716659707
[Paper] [BibTex] - Identifying Unexpected Behaviors of Agent-based Models through Spatial Plots and Heat Maps
C.J. Lynch, H. Kavak, D. Vernon-Bido, and R.J. Gore
Swarmfest 2017, Suffolk, VA, August 11-13, 2017
[Paper] [BibTex]
Last updated on Jan 30, 2022.